Highlights
- This report provides information on unaudited spending by the Province through the first quarter of the 2023-24 fiscal year (April 1, 2023 to June 30, 2023).
- The information in this report is based on the FAO’s analysis of transactions recorded in the Province’s Integrated Financial Information System (IFIS) as of June 30, 2023. All figures are unaudited, as final audited figures are not available until the release of the Public Accounts of Ontario after the end of the 2023-24 fiscal year.
2023-24 Spending Plan
- The Province’s yearly spending plan represents the legal spending authority for ministries as granted by the Legislature through the process of supply.[1] The Province started the 2023-24 fiscal year with a spending plan of $197.3 billion.[2]
Changes to the 2023-24 Spending Plan
- The Province may change its spending plan throughout the year, either by requesting additional spending authority from the Legislature or by reallocating spending among different programs through Treasury Board Orders.
- As of the end of the first quarter, the Province’s spending plan was down $32 million to $197.3 billion.
- By sector, the largest spending plan increase during the first quarter was in ‘other programs,’ at $604 million, followed by justice ($190 million), children, community and social services ($33 million), education ($2 million) and postsecondary education ($1 million). This was more than offset by a $14 million reduction in the health sector spending plan and an $849 million transfer from the Contingency Fund.
First Quarter Spending: Actual Unaudited Spending vs. Planned Spending
- In order to manage and monitor its program spending during the fiscal year, the Province divides its spending plan into planned spending by quarter, which reflects historical spending patterns, seasonality and other factors. In 2023-24, the Province plans to spend $42.8 billion in the first quarter, $43.5 billion in the second quarter, $46.3 billion in the third quarter and $64.7 billion in the fourth quarter.[3]
- Although the Province planned to spend $42.8 billion in the first quarter of 2023-24, actual unaudited spending was $40.2 billion. Overall, this was $2.6 billion (6.1 per cent) less than planned.
- Most sectors spent less than planned, led by health (-$1,194 million or 6.5 per cent), ‘other programs’ (‑$1,008 million or 14.3 per cent), interest on debt (-$244 million or 7.1 per cent), postsecondary education (‑$160 million or 9.8 per cent) and children, community and social services (-$108 million or 2.3 per cent).
- Two sectors spent more than planned: justice ($95 million or 7.4 per cent) and education ($25 million or 0.4 per cent).
- For information on spending by all of the Province’s programs and ministries, visit the FAO’s website at: https://tinyurl.com/2xmjbnnw.
First Quarter Spending: 2023-24 Spending vs. 2022-23 Spending
- This report also compares 2023-24 actual unaudited spending against 2022-23 spending to provide context for provincial spending trends and to identify significant year-over-year spending changes.
- Spending in the first quarter of the 2023-24 fiscal year was $296 million (0.7 per cent) higher than during the same period in 2022-23.
- The largest year-over-year spending increase was in ‘other programs’ ($720 million or 13.5 per cent), followed by education ($428 million or 7.2 per cent), children, community and social services ($274 million or 6.3 per cent), justice ($80 million or 6.1 per cent) and postsecondary education ($3 million or 0.2 per cent). Conversely, two sectors spent less in the first quarter of 2023-24 than during the same period in 2022-23: health (-$1,056 million or 5.8 per cent) and interest on debt (-$153 million or 4.6 per cent).
Status of the Contingency Fund
- The Contingency Fund is used to address spending pressures or fund program changes during the fiscal year. The funds within the Contingency Fund cannot be spent directly by the Province but must be transferred to government programs through Treasury Board Orders.
- The Province started the 2023-24 fiscal year with a total of $4.0 billion in the Contingency Fund. In the first quarter, the Province transferred $849 million from the Contingency Fund to various programs. At the end of the first quarter, the Contingency Fund had a remaining balance of $3.2 billion.
Introduction
This report provides information on spending by the Government of Ontario (the Province) through the first quarter of the 2023-24 fiscal year, from April 1, 2023 to June 30, 2023. The report:
- identifies changes made to the Province’s 2023-24 spending plan during the first quarter;
- reviews actual unaudited spending in the first quarter of 2023-24 against both the Province’s spending plan and actual spending during the first quarter of 2022-23; and
- tracks transfers from the Province’s Contingency Fund.
The information in this report is based on the FAO’s analysis of transactions recorded in the Province’s Integrated Financial Information System (IFIS) as of June 30, 2023. All figures are unaudited, as final audited figures are not available until the release of the Public Accounts of Ontario up to six months after the end of the fiscal year.
2023-24 Spending Plan
The Province’s yearly spending plan represents the legal spending authority for ministries as granted by the Legislature through the process of supply.[4] The Province started the 2023-24 fiscal year with a spending plan of $197.3 billion.[5]
Changes to the 2023-24 Spending Plan
The Province may change its spending plan throughout the year, either by requesting additional spending authority from the Legislature or by reallocating spending among different programs through Treasury Board Orders. As of the end of the first quarter, June 30, 2023, the Province’s spending plan was down $32 million.
By sector, the largest spending plan increase during the first quarter of 2023-24 was in ‘other programs,’ at $604 million, followed by justice ($190 million), children, community and social services ($33 million), education ($2 million) and postsecondary education ($1 million). This was more than offset by a $14 million reduction in the health sector spending plan and an $849 million transfer from the Contingency Fund.
| Sector | 2023-24 Spending Plan |
Q1 Changes | Revised 2023-24 Spending Plan | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Health | 77,090 | -14 | 77,076 | |
| Education | 36,281 | 2 | 36,283 | |
| Postsecondary Education | 7,226 | 1 | 7,228 | |
| Children, Community and Social Services | 19,526 | 33 | 19,559 | |
| Justice | 5,664 | 190 | 5,854 | |
| Other Programs | 33,756 | 604 | 34,360 | |
| Unallocated Funds: | ||||
| Contingency Fund | 4,000 | -849 | 3,151 | |
| Interest on Debt | 13,764 | - | 13,764 | |
| Total | 197,307 | -32 | 197,275 | |
First Quarter Analysis
This section highlights key first quarter spending plan changes by sector and vote-item. For information on all of the Province’s transfer payment programs and ministries, visit the FAO’s website at: https://tinyurl.com/2xmjbnnw.
Health: $14 million decrease. Notable changes include:
- $214 million increase for Health Services (Vote-Item 1416-1), for the Operation of Hospitals.
- $241 million decrease for Provincial Programs (Vote-Item 1412-1), for Community and Priority Services.
Justice: $190 million increase. Notable changes include:
- $44 million increase for Ontario Provincial Police, Corporate and Strategic Services (Vote-Item 2604-1).
- $24 million increase for Ontario Provincial Police, Investigations and Organized Crime (Vote-Item 2604-3).
- $23 million increase for Ministry of the Solicitor General, Ministry Administration (Vote-Item 2601-1).
- $23 million increase for Ministry of the Solicitor General, Public Safety Division, External Relations Branch (Vote-Item 2603-5).
Other Programs: $604 million increase. Notable changes include:
- $358 million increase for Economic Development, Job Creation and Trade (Vote-Item 902-13), for Industrial Land Development ($158 million) and Services ($200 million), for investments in the electric vehicle battery manufacturing sector.
- $50 million increase for Ministry of Infrastructure, Infrastructure Partnership Projects and Agency Oversight (Vote-Item 4007-1), largely for Transit-Oriented Communities.
- $50 million increase for Ministry of Transportation, Transit (Operating) (Vote-Item 2702-2), for Metrolinx Operating Subsidies.
- A net $146 million increase for 67 additional vote-items in the ‘other programs’ sector. For more information, visit the FAO’s website at: https://tinyurl.com/2xmjbnnw.
Actual Unaudited Spending to Date
Actual Unaudited Spending vs. Planned Spending
In order to manage and monitor its program spending during the fiscal year, the Province divides its spending plan into planned spending by quarter, which reflects historical spending patterns, seasonality and other factors. For 2023-24, the Province plans to spend $42.8 billion in the first quarter, $43.5 billion in the second quarter, $46.3 billion in the third quarter and $64.7 billion in the fourth quarter.[6]
For the first quarter of 2023-24, the Province planned to spend $42.8 billion but actual unaudited spending was $40.2 billion. This was $2.6 billion (6.1 per cent) less than planned.
Figure 12023-24 actual unaudited spending vs planned spending, by quarter, $ millions
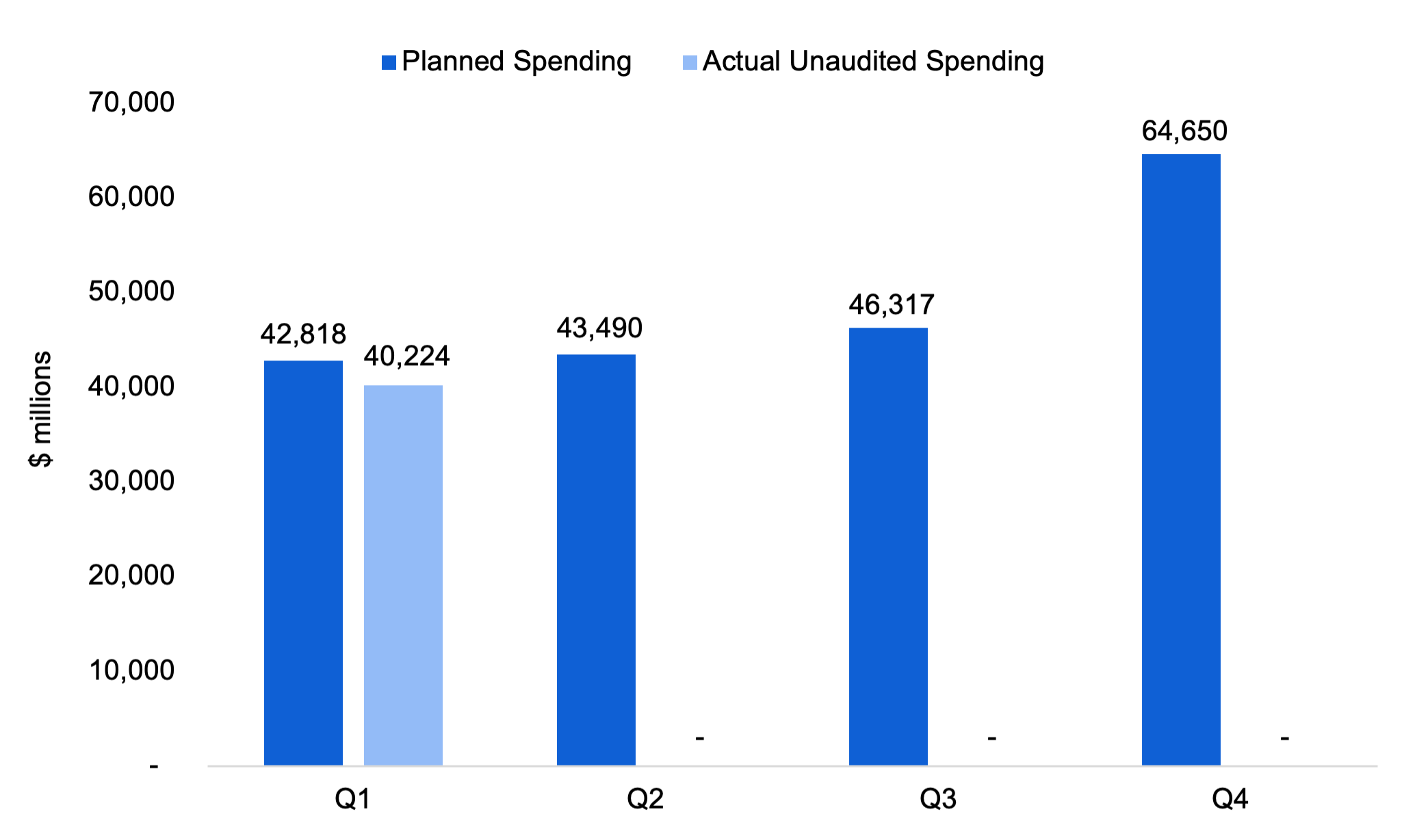
Note: Figures exclude spending on some assets and additional spending by the broader public sector organizations controlled by the Province (hospitals, school boards and colleges), the Province’s agencies and the legislative offices. Planned fourth quarter spending is significantly higher than planned spending in each of the first three quarters due to year-end accrual adjustments.
FAO analysis of information provided by Treasury Board Secretariat.
By sector, the first quarter lower-than-planned spending was led by health (-$1,194 million, 6.5 per cent), ‘other programs’ (-$1,008 million, 14.3 per cent), interest on debt (-$244 million, 7.1 per cent), postsecondary education (-$160 million, 9.8 per cent) and children, community and social services (-$108 million, 2.3 per cent). Spending was above plan for two sectors: justice ($95 million, 7.4 per cent) and education ($25 million, 0.4 per cent).
| Sector | Revised 2023-24 Spending Plan | Planned Spending at end of Q1 | Actual Unaudited Spending at end of Q1 | Actual vs. Planned at end of Q1 | Actual vs. Planned (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Health | 77,076 | 18,360 | 17,165 | -1,194 | -6.5% | |
| Education | 36,283 | 6,363 | 6,388 | 25 | 0.4% | |
| Postsecondary Education | 7,228 | 1,627 | 1,467 | -160 | -9.8% | |
| Children, Community and Social Services | 19,559 | 4,702 | 4,594 | -108 | -2.3% | |
| Justice | 5,854 | 1,290 | 1,385 | 95 | 7.4% | |
| Other Programs | 34,360 | 7,044 | 6,036 | -1,008 | -14.3% | |
| Unallocated Funds: | ||||||
| Contingency Fund | 3,151 | - | - | - | N/A | |
| Interest on Debt | 13,764 | 3,432 | 3,189 | -244 | -7.1% | |
| Total | 197,275 | 42,818 | 40,224 | -2,594 | -6.1% | |
The rest of this section highlights key vote-item spending that was above and below plan in the first quarter of 2023-24. For information on spending by all of the Province’s programs and ministries, visit the FAO’s website at: https://tinyurl.com/2xmjbnnw.
Health sector spending: $1,194 million (6.5 per cent) less than planned. Highlights include:
- $163 million higher than planned in Health Services (Vote-Item 1416-1), which funds the operation of hospitals, home care, community services and other services.
- $106 million higher than planned in Ontario Health Insurance (Vote-Item 1405-1), which administers payments to physicians.
- $203 million less than planned in Health Capital Program (Vote-Item 1407-1), which provides capital funding to hospitals and other health care facilities.
- $326 million less than planned in Long-Term Care Homes Program (Operating) (Vote-Item 4502-1), which funds the operation and development of long-term care homes.
- $875 million less than planned in Drug Programs (Vote-Item 1405-2), which funds a number of provincial drug programs, the largest of which is the Ontario Drug Benefit program. Ministry of Health staff noted that the less-than-planned spending is largely due to a delay in posting June 2023 payments.
Education sector spending: $25 million (0.4 per cent) higher than planned. Highlights include:
- $133 million higher than planned in Elementary and Secondary Education Program – Policy and Program Delivery (Vote-Item 1002-1), which mainly funds school boards.
- $79 million less than planned in Child Care and Early Years Programs – Policy Development and Program Delivery (Vote-Item 1004-1), which includes the Province’s commitment to provide an average of $10-a-day child care by 2025.
Postsecondary education sector spending: $160 million (9.8 per cent) less than planned. Highlights include:
- $72 million less than planned in Colleges, Universities and Student Support (Vote-Item 3002-1), which provides operating grants for colleges and universities, and student financial assistance programs.
- $91 million less than planned in Support for Postsecondary Education (Capital) (Vote-Item 3002-3), which provides capital grants to colleges, universities and Indigenous Institutes.
Children, community and social services sector spending: $108 million (2.3 per cent) less than planned. Highlights include:
- $75 million less than planned in Financial and Employment Supports (Vote-Item 702-3), which includes the Ontario Disability Support Program, Ontario Works and the Ontario Drug Benefit Plan.
Justice sector spending: $95 million (7.4 per cent) higher than planned across a number of programs.
Other Programs sector spending: $1,008 million (14.3 per cent) less than planned. Highlights include:
- $203 million higher than planned in Ministry of Transportation, Transit (Capital) (Vote-Item 2702-3), which mainly provides capital funding for Metrolinx and municipal transit infrastructure projects.
- $117 million less than planned in Ministry of Infrastructure, Infrastructure Programs (Capital) (Vote-Item 4003-2), which funds infrastructure programs, such as Broadband and Cellular Infrastructure and various Federal-Provincial programs.
- $658 million less than planned in Ministry of Energy, Electricity Price Mitigation (Vote-Item 2905-1), which includes electricity subsidy programs such as the Ontario Electricity Rebate and Comprehensive Electricity Plan.
- A net $436 million less than planned in the remaining 326 vote-items in the ‘other programs’ sector. For more information, visit the FAO’s website at: https://tinyurl.com/2xmjbnnw
2023-24 Spending vs. 2022-23 Spending
This report also compares 2023-24 actual unaudited spending against 2022-23 spending to provide context for provincial spending trends and to identify significant year-over-year spending changes.
As noted above, in the first quarter of 2023-24, the Province spent $40.2 billion. This was $0.3 billion (0.7 per cent) more than was spent in the first quarter of 2022-23. The largest year-over-year spending increase was in ‘other programs’ ($720 million, 13.5 per cent), followed by education ($428 million, 7.2 per cent), children, community and social services ($274 million, 6.3 per cent), justice ($80 million, 6.1 per cent) and postsecondary education ($3 million, 0.2 per cent). Conversely, two sectors had year-over-year spending decreases: health (‑$1,056 million, 5.8 per cent) and interest on debt (-$153 million, 4.6 per cent).
| Sector | 2023-24 Spending at end of Q1 |
2022-23 Spending at end of Q1 | 2023-24 vs. 2022-23 |
2023-24 vs. 2022-23 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Health | 17,165 | 18,221 | -1,056 | -5.8% |
| Education | 6,388 | 5,960 | 428 | 7.2% |
| Postsecondary Education | 1,467 | 1,465 | 3 | 0.2% |
| Children, Community and Social Services | 4,594 | 4,320 | 274 | 6.3% |
| Justice | 1,385 | 1,305 | 80 | 6.1% |
| Other Programs | 6,036 | 5,317 | 720 | 3.5% |
| Interest on Debt | 3,189 | 3,341 | -153 | -4.6% |
| Total | 40,224 | 39,928 | 296 | 0.7% |
- The health sector spent $1,056 million (5.8 per cent) less in the first quarter of 2023-24 compared to the first quarter of 2022-23, largely due to lower spending for:
- payments to physicians (-$150 million);
- Major Hospitals Projects (-$184 million);
- Population and Public Health (Vote-Item 1406-4) (-$322 million), largely due to lower spending on Official Local Health Agencies (-$66 million) and the conclusion of the COVID-19 Response program in 2022-23 (-$243 million); and
- Drug Programs (Vote-Item 1405-2) (-$365 million).
- The education sector spent $428 million (7.2 per cent) more in the first quarter of 2023-24 compared to the first quarter of 2022-23, largely due to higher spending for:
- School Board Operating Grants ($239 million); and
- the Child Care and Early Years program ($138 million), which includes the Province’s commitment to provide an average of $10-a-day child care by 2025.[7]
- The children, community and social services sector spent $274 million (6.3 per cent) more in the first quarter of 2023-24 compared to the first quarter of 2022-23, largely due to higher spending for:
- Ontario Works – Financial Assistance ($88 million);
- Autism ($77 million); and
- the Ontario Disability Support Program – Financial Assistance ($58 million).
- The justice sector spent $80 million (6.1 per cent) more in the first quarter of 2023-24 compared to the first quarter of 2022-23, due to higher spending on a variety of programs.
- The other programs sector spent $720 million (13.5 per cent) more in the first quarter of 2023-24 compared to the first quarter of 2022-23, largely due to higher spending for:
- Ministry of Transportation, Metrolinx infrastructure projects ($673 million);
- Ministry of Transportation, Metrolinx operating subsidies ($131 million); and
- Ministry of Finance, Guaranteed Annual Income System ($46 million);
- offset by lower spending on:
- Ministry of Energy, the Ontario Electricity Rebate (-$230 million).
- Interest on debt spending was $153 million (4.6 per cent) less in the first quarter of 2023-24 compared to the first quarter of 2022-23.
Status of the Contingency Fund
The Contingency Fund is used to address spending pressures or fund program changes during the fiscal year. The funds within the Contingency Fund cannot be spent directly by the Province but must be transferred to government programs through Treasury Board Orders.
The Province started the 2023-24 fiscal year with a total of $4.0 billion in the Contingency Fund. In the first quarter, the Province transferred $849 million from the Contingency Fund to various programs. This results in a remaining balance in the Contingency Fund, as of June 30, of $3.2 billion.
| Ministry/Program | $ millions | ||
| Opening Contingency Fund Balance | 4,000 | ||
| Less: First Quarter Transfers to Ministries | |||
| Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs | |||
| Ontario Wine Fund | -10 | ||
| Better Public Health and Environment | >-1 | ||
| Policy Development | >-1 | ||
| Ministry Administration | >-1 | ||
| Research | >-1 | ||
| Ministry of the Attorney General | |||
| Ministry Administration | -11 | ||
| Criminal Law | -6 | ||
| Administration of Justice | -5 | ||
| Judicial Services | -1 | ||
| Indigenous Justice | >-1 | ||
| Cabinet Office | |||
| Main Office | -5 | ||
| Ministry of Children, Community and Social Services | |||
| Family Responsibility Office | -3 | ||
| Children, Youth and Social Services Information and Information Technology Cluster | -3 | ||
| Ministry of Citizenship and Multiculturalism | |||
| Ministry Administration | -3 | ||
| Anti-Racism Directorate | >-1 | ||
| Citizenship, Inclusion and Heritage | >-1 | ||
| Ministry of Colleges and Universities | |||
| Ministry Administration | >-1 | ||
| Research Support Operating Expense | >-1 | ||
| Colleges, Universities and Student Support | >-1 | ||
| Ministry of Economic Development, Job Creation and Trade | |||
| Industrial Land Development | -158 | ||
| Economic Development, Job Creation and Trade – Services | -200 | ||
| Ministry of Education | |||
| Child Care And Early Years Program – Policy Development and Program Delivery | -1 | ||
| Elementary and Secondary Education Program – Policy and Program Delivery | >-1 | ||
| Ministry Administration | >-1 | ||
| Ministry of Energy | |||
| Ministry Administration | >-1 | ||
| Ministry of the Environment, Conservation and Parks | |||
| Ontario Parks | >-1 | ||
| Environmental Compliance and Enforcement | >-1 | ||
| Environmental Sciences and Standards | >-1 | ||
| Ministry Administration | >-1 | ||
| Environmental Policy and Programs | >-1 | ||
| Environmental Assessment and Permissions | >-1 | ||
| Conservation and Water Protection | >-1 | ||
| Climate Change and Resiliency | >-1 | ||
| Indigenous Drinking Water Program | >-1 | ||
| Ministry of Finance | |||
| Tax and Benefits Administration | -2 | ||
| Ministry of Francophone Affairs | |||
| Francophone Affairs Co-ordination | >-1 | ||
| Ministry of Health | |||
| Stewardship | -2 | ||
| Ministry Administration | -1 | ||
| Population and Public Health | >-1 | ||
| Emergency Health services | >-1 | ||
| IT Services – Health Cluster | >-1 | ||
| Ontario Health Insurance | >-1 | ||
| Drug Programs | >-1 | ||
| Digital Health and Information Management | >-1 | ||
| Health Policy and Research | >-1 | ||
| Ministry of Indigenous Affairs | |||
| Indigenous Affairs | -2 | ||
| Ministry Administration | -1 | ||
| Ministry of Infrastructure | |||
| Transit-Oriented Communities | -50 | ||
| Toronto Waterfront Revitalization Corporation (Capital) | -25 | ||
| Ministry Administration | -2 | ||
| Infrastructure Policy, Planning and Projects | -1 | ||
| Legislative Building Reconstruction | >-1 | ||
| Government Real Estate | >-1 | ||
| Infrastructure Partnership Projects and Agency Oversight | >-1 | ||
| Ministry of Labour, Immigration, Training and Skills Development | |||
| Ministry Administration | -3 | ||
| Employment Ontario System | -1 | ||
| Ministry of Long-Term Care | |||
| Ministry Administration | -4 | ||
| Long-Term Care Homes Program | -3 | ||
| Ministry of Mines | |||
| Ministry Administration | >-1 | ||
| Mineral Sector Competitiveness | >-1 | ||
| Ministry of Municipal Affairs and Housing | |||
| Priority Projects for Municipalities and Municipal Organizations (Capital) | -24 | ||
| Community and Market Housing | -3 | ||
| Ministry Administration | -1 | ||
| Ministry of Natural Resources and Forestry | |||
| Sustainable Resource Management | -2 | ||
| Ministry Administration | -1 | ||
| Land and Resources Information Technology Cluster | >-1 | ||
| Ministry of Northern Development | |||
| Ministry Administration | >-1 | ||
| Northern Economic Development | >-1 | ||
| Ministry of Public and Business Service Delivery | |||
| Consumer Services | -8 | ||
| Enterprise Information and Information Technology Services | -2 | ||
| ServiceOntario | -1 | ||
| Enterprise Business and Financial Services | >-1 | ||
| Information, Privacy and Archives | >-1 | ||
| Government Services Integration Cluster | >-1 | ||
| Ontario Digital Services | >-1 | ||
| Ministry Administration | >-1 | ||
| Ministry for Seniors and Accessibility | |||
| Ministry Administration | -1 | ||
| Policy, Program, and Strategic Partnerships | >-1 | ||
| Accessibility for Ontarians with Disabilities | >-1 | ||
| Ministry of the Solicitor General | |||
| Corporate and Strategic Services | -44 | ||
| Emergency Planning and Management (Capital Asset) | -33 | ||
| Investigations and Organized Crime | -24 | ||
| Ministry Administration | -23 | ||
| Fleet Management | -22 | ||
| Federal-Provincial First Nations Policing Agreement (Capital) | -16 | ||
| Miscellaneous Grants – Policing Services | -14 | ||
| Field and Traffic Services | -13 | ||
| Federal-Provincial First Nations Policing Agreement (Operating) | -8 | ||
| External Relations Branch – Transportation and Communications | -1 | ||
| Office of the Fire Marshal and Emergency Management | >-1 | ||
| Ministry of Tourism, Culture and Sport | |||
| Grants in Support of the Festival and Event Attractions and Support Program | -3 | ||
| Tourism and Culture Programs – Salaries and Wages | >-1 | ||
| Ministry Administration | >-1 | ||
| Agency Programs | >-1 | ||
| Sport, Recreation and Community | >-1 | ||
| Ministry of Transportation | |||
| Metrolinx Operating Subsidies | -50 | ||
| Business Support | -4 | ||
| Office of the Lieutenant Governor | |||
| Office of the Lieutenant Governor | >-1 | ||
| Treasury Board Secretariat | |||
| Labour Relations and Compensation | -24 | ||
| Centre for People, Culture and Talent | -2 | ||
| Central Agencies Cluster | >-1 | ||
| Office of the Comptroller General | >-1 | ||
| Emergency Management Ontario | >-1 | ||
| Supply Chain Transformation Office | >-1 | ||
| Ministry Administration | >-1 | ||
| Treasury Board Support and Financial Planning | >-1 | ||
| Total First Quarter Transfers to Ministries | -849 | ||
| Contingency Fund Balance as of June 30, 2023 | 3,151 | ||
Graphical Descriptions
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planned Spending | 42,818 | 43,490 | 46,317 | 64,650 | |
| Actual Unaudited Spending | 40,224 | - | - | - | |
Footnotes
[1] Temporary spending authority is first granted by the Legislature through the Interim Appropriation Act, with final spending authority then granted through the Supply Act. Permanent spending authority is also granted through other legislation for a limited number of programs.
[2] The $197.3 billion spending plan excludes $7.4 billion in additional planned spending by the broader public sector organizations controlled by the Province (hospitals, school boards and colleges), the Province’s agencies and the legislative offices. The $7.4 billion in additional planned spending is not reviewed in this report as the Province does not actively monitor or control this spending. As well, the $197.3 billion spending plan excludes $1.4 billion in planned spending on operating assets and $4.7 billion in planned spending on capital assets.
[3] Planned fourth quarter spending is significantly higher than planned spending in each of the first three quarters due to year-end accrual adjustments.
[4] Temporary spending authority is first granted by the Legislature through the Interim Appropriation Act, with final spending authority then granted through the Supply Act. Permanent spending authority is also granted through other legislation for a limited number of programs.
[5] The $197.3 billion spending plan excludes $7.4 billion in additional planned spending by the broader public sector organizations controlled by the Province (hospitals, school boards and colleges), the Province’s agencies and the legislative offices. The $7.4 billion in additional planned spending is not reviewed in this report as the Province does not actively monitor or control this spending. As well, the $197.3 billion spending plan excludes $1.4 billion in planned spending on operating assets and $4.7 billion in planned spending on capital assets.
[6] Planned fourth quarter spending is significantly higher than planned spending in each of the first three quarters due to year-end accrual adjustments.
[7] For more analysis see FAO, “Ministry of Education: Spending Plan Review,” 2022.

